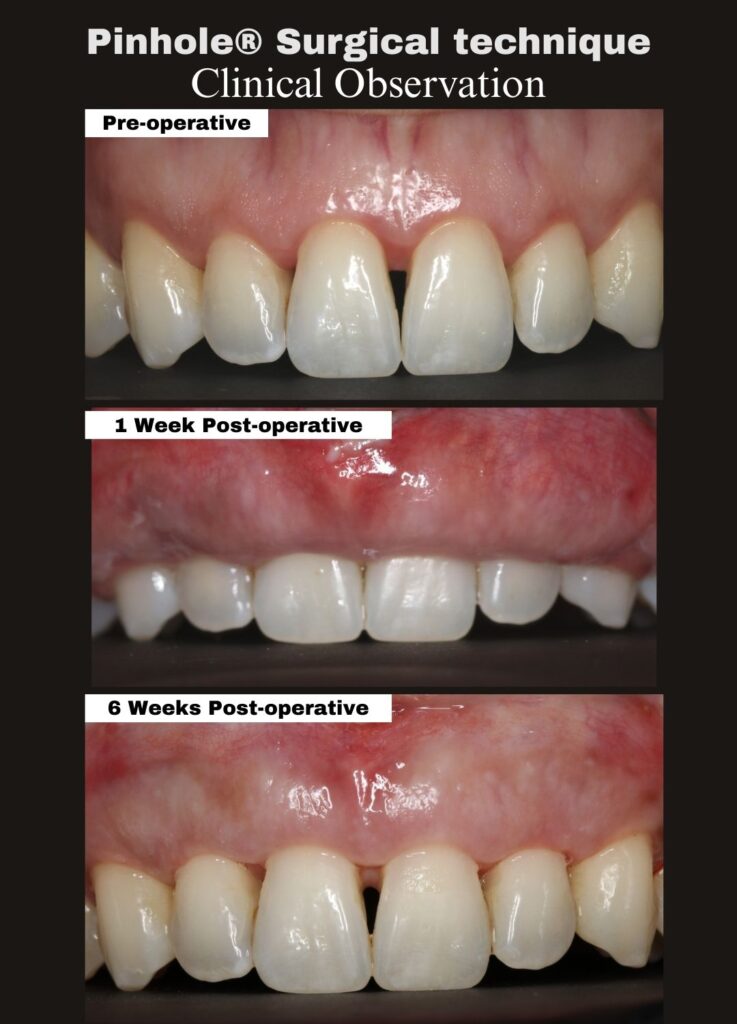
We’re pleased to share a 2-month clinical follow-up demonstrating continued healing and gingival stability following treatment with the Pinhole® Surgical Technique (PST).
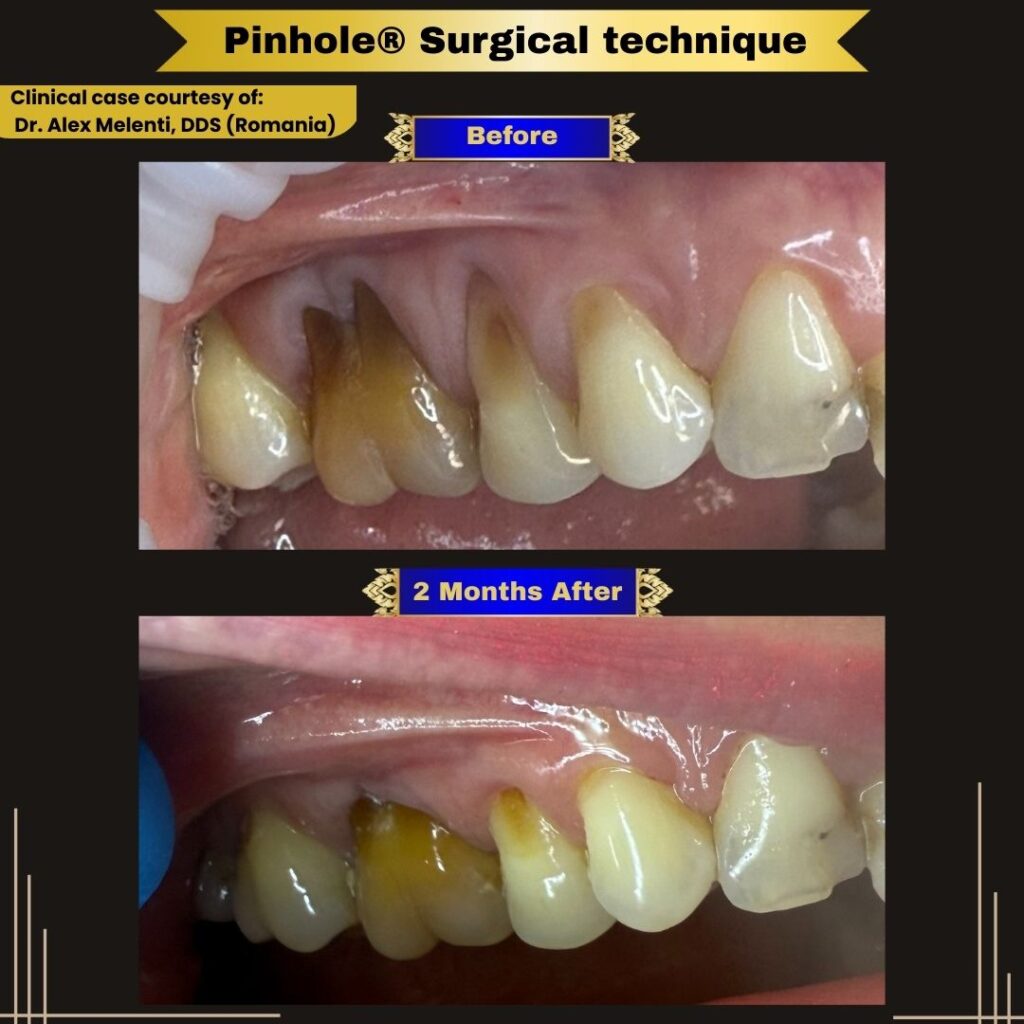
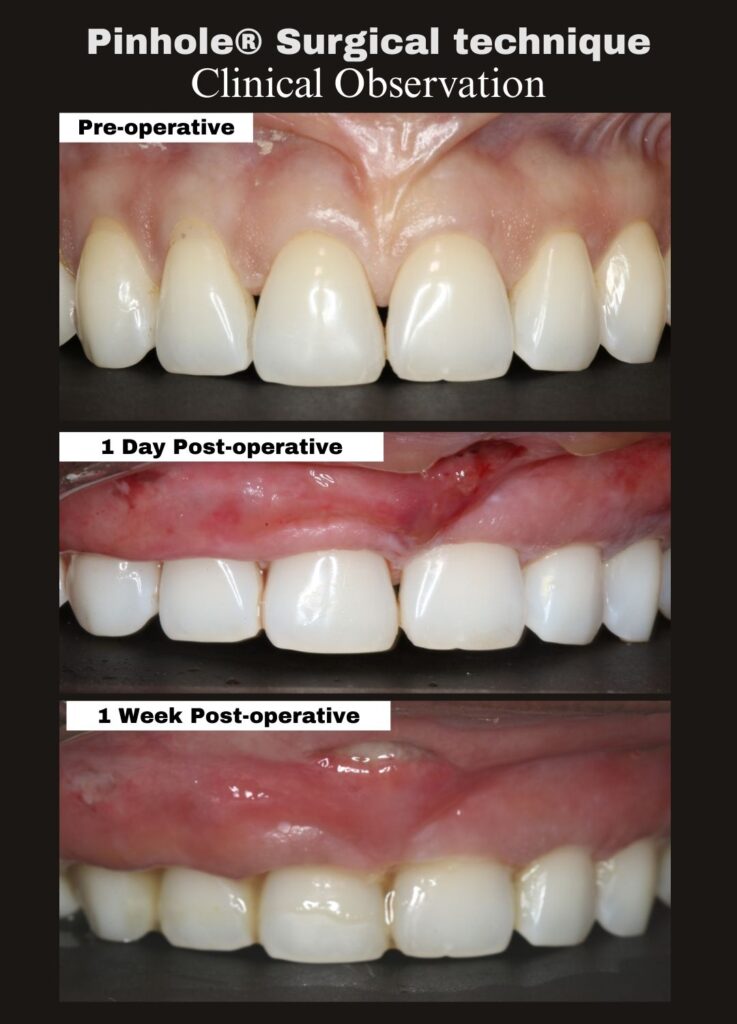
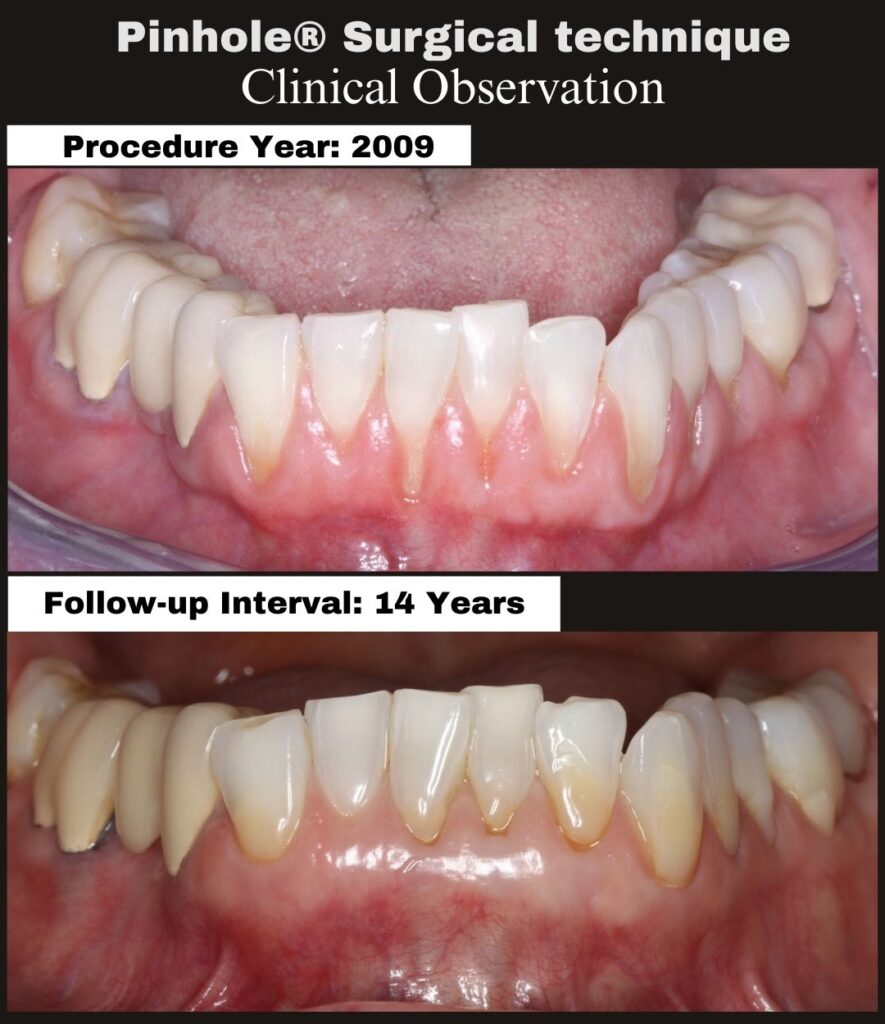
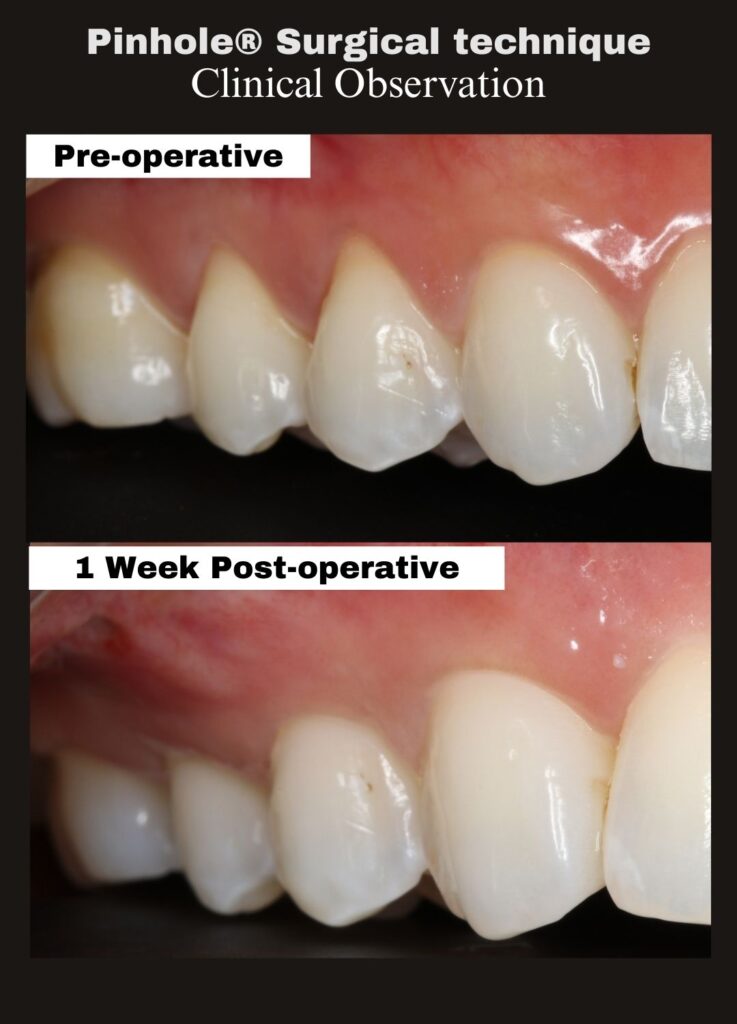
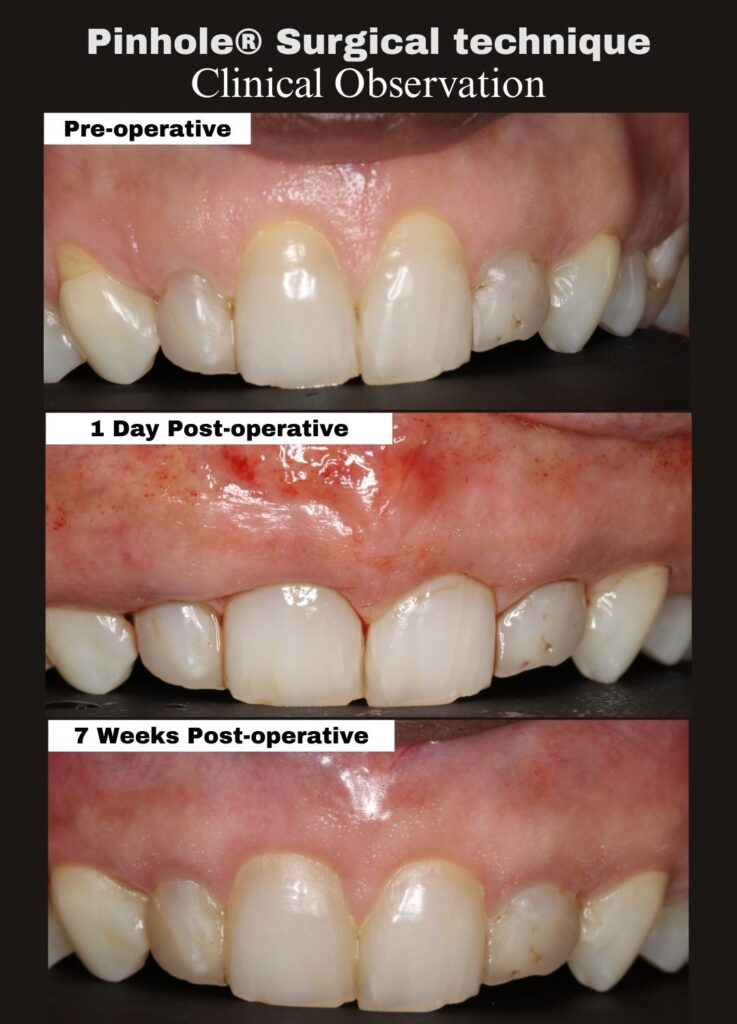
This case, performed by Dr. Alex Melenti (Romania), highlights the biologic healing process that continues well beyond the immediate post-operative period. At two months, the treated sites show improved gingival position, healthier tissue appearance, and encouraging early stability—consistent with expected PST healing patterns.
Immediate post-operative gingival position is not intended to represent the final outcome. Instead, final tissue position and contour continue to evolve as healing and maturation progress over time.
We congratulate Dr. Melenti on these excellent early results and thank him for contributing his case to the professional PST community.
Sharing Strengthens the Community
We welcome case submissions from Pinhole-trained doctors. If you would like to share your clinical results—early healing, mid-term follow-ups, or long-term outcomes—please send your cases to PSTAcademy@gmail.com.
Case images courtesy of Dr. Alex Melenti, DDS (Romania).